Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit
Despite being a preventable and treatable disease, TB remains a major challenge for global health. One of the biggest challenges in TB control is the emergence of drug-resistant TB strains. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) are forms of TB that do not respond to first-line drugs and are more difficult and expensive to treat.
Another challenge is the high rate of TB-HIV co-infection. People living with HIV have weakened immune systems, which makes them more susceptible to TB infection. In fact, TB is one of the leading causes of death among people living with HIV.
In addition, TB is often underdiagnosed and undertreated, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where resources are limited. Many people with TB do not seek medical care due to stigma or lack of awareness, and many cases go undiagnosed or are diagnosed too late.

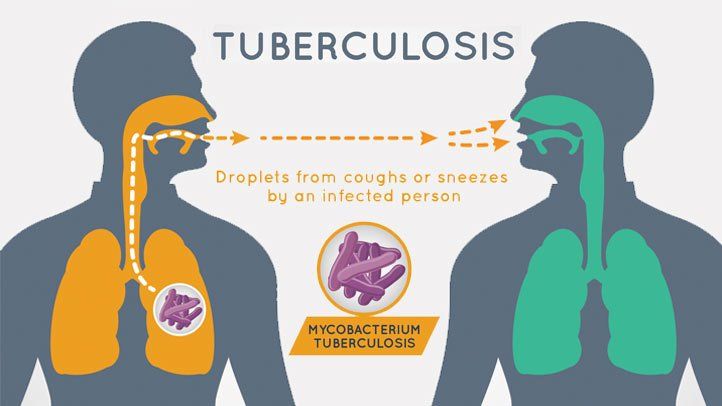
Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective TB control. Early detection and treatment not only improves the chances of a full recovery, but also reduces the spread of TB to others.
There are several diagnostic tools available for TB, including chest X-rays, sputum tests, and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs). The most commonly used test for TB diagnosis is the sputum test, which involves analyzing a sample of sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs) under a microscope to detect the presence of TB bacteria.
However, sputum tests can produce false negatives, particularly in people with HIV or who have extrapulmonary TB. In these cases, other diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays or IGRAs may be used.
In recent years, there have been several technological advancements in TB diagnosis, such as the GeneXpert MTB/RIF test, which is a rapid molecular test that can detect TB bacteria and rifampicin resistance in less than 2 hours.
In addition to early detection, it is also important to ensure that patients receive prompt and appropriate treatment for TB. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics for a period of 6-9 months. It is important that patients adhere to the full course of treatment to ensure complete eradication of the TB bacteria and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
TB remains a significant global health challenge, with drug-resistant strains and high rates of co-infection with HIV contributing to its persistence. Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective TB control, and there are several diagnostic tools available for this purpose. Early detection and prompt treatment not only improve patient outcomes, but also help prevent the spread of TB to others. It is important for health systems to prioritize TB control efforts and ensure that patients receive the care they need.